Berkelium
97
Bk
Gruppe
i/t
Periode
7
Blokk
f
Proton
Elektron
Nøytron
97
97
150
Generelle eigenskapar
Atomnummer
97
Atommasse
[247]
Massetal
247
Kategori
Aktinid
Farge
i/t
Radioaktiv
Ja
Named after Berkeley, California, the city of its discovery
Krystallstruktur
Enkel heksagonal
Historie
Berkelium was discovered by Glenn T. Seaborg, Albert Ghiorso and Stanley G. Thompson in 1949 at the University of California, Berkeley.
It was produced by the bombardment of americium with alpha particles.
Berkelium was isolated in greater quantities for the first time by Burris Cunningham and Stanley Thompson in 1958.
It was produced by the bombardment of americium with alpha particles.
Berkelium was isolated in greater quantities for the first time by Burris Cunningham and Stanley Thompson in 1958.
Elektron per energinivå
2, 8, 18, 32, 27, 8, 2
Elektronkonfigurasjon
[Rn] 5f9 7s2
Just over one gram of berkelium has been produced in the United States since 1967
Fysiske eigenskapar
Tilstandsform
Fast stoff
Tettleik
14,78 g/cm3
Smeltepunkt
1259,15 K | 986 °C | 1806,8 °F
Kokepunkt
3173,15 K | 2900 °C | 5252 °F
Smeltevarme
i/t kJ/mol
Fordampingsvarme
i/t kJ/mol
Spesifikk varmekapasitet
- J/g·K
Førekomst i jordskorpa
i/t
Førekomst i universet
i/t
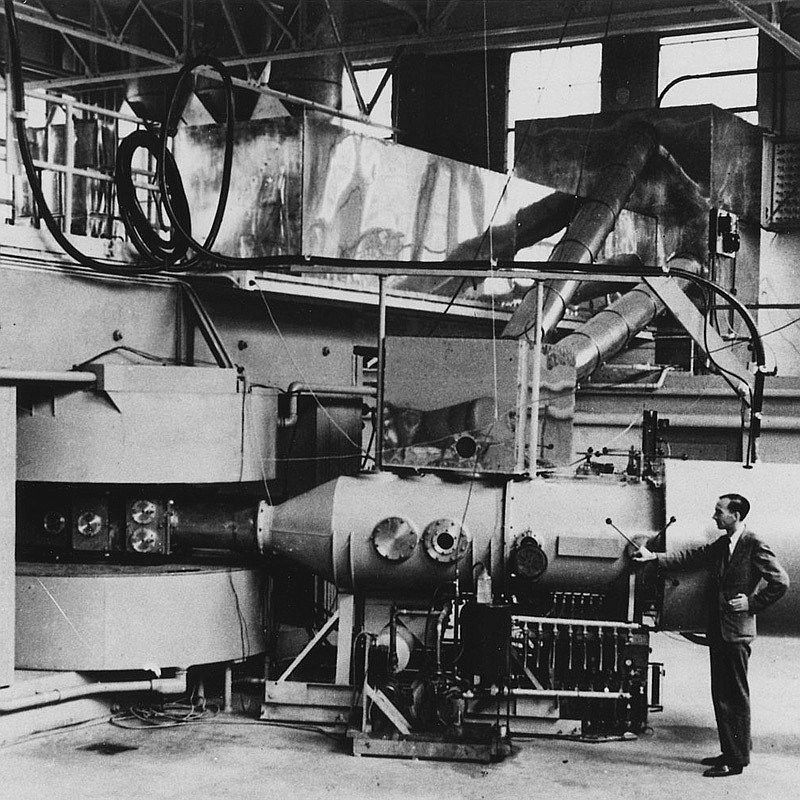
Biletkreditering: Wikimedia Commons (Department of Energy - Office of Public Affairs)
The 60-inch cyclotron at the Lawrence Radiation Laboratory, University of California, Berkeley
CAS-nummer
7440-40-6
PubChem CID-nummer
23971
Atom eigenskapar
Atomradius
170 pm
Kovalent radius
-
Elektronegativitet
1,3 (Paulings skala)
Ioniseringspotensial
6,1979 eV
Molart volum
16,7 cm3/mol
Termisk konduktivitet
0,1 W/cm·K
Oksidasjonstrinn
3, 4
Bruksområde
Berkelium is mainly used for scientific research purposes.
Berkelium-249 is a common target nuclide to prepare still heavier transuranic elements and transactinides, such as lawrencium, rutherfordium and bohrium.
It is also useful as a source of the isotope californium-249.
Berkelium-249 is a common target nuclide to prepare still heavier transuranic elements and transactinides, such as lawrencium, rutherfordium and bohrium.
It is also useful as a source of the isotope californium-249.
Berkelium is harmful due to its radioactivity
Isotopar
Stabile isotopar
-Ustabile isotopar
233Bk, 235Bk, 236Bk, 237Bk, 238Bk, 239Bk, 240Bk, 241Bk, 242Bk, 243Bk, 244Bk, 245Bk, 246Bk, 247Bk, 248Bk, 249Bk, 250Bk, 251Bk, 252Bk, 253Bk, 254Bk